Network model
Due to large number of existing programming switches (cCS), there is a separation to 3 levels for the purpose of accessibility and simplification of control over large number of elements.
Due to large number of existing programming switches (cCS), there is a separation to 3 levels for the purpose of accessibility and simplification of control over large number of elements. On Pic 2 there is an example of connection between subscribers various TS.
LEVEL1 is represented with nonduplicated cCS, the purpose of which is local connection of subscribers and analogueue interfaces. They connect to neighbouring cCS (left and right) for the purpose of provision of connection between sites. They connect to duplicated cCS on LEVEL2 and to the reserve cCS on LEVEL2. The LEVEL1 station can in exceptional circumstances act as a control station.
LEVEL2 is represented by duplicated cCS. They serve the purpose of provision of connection for stations of LEVEL1, connected via transit stations of LEVEL3. All stations of LEVEL2 of one TS are connected between each other and the reserve station. Stations of LEVEL2 are controlling stations and provide the following functions OTC: Sustaining one or several circuits
Operators ISDN and operators IP are subscribers of the cCS, which sustains the circuit of that operator. Provision of interaction through interface E1 with existing systems OTC using special signalling DSS under standard DX500.
LEVEL3 is represented by two nonduplicated cCS, which provide special reservation of transit connections. They provide connection between sites of LEVEL2 of different TS, including reserve stations. They also provide the option of connecting contiguous sites in the future after their transfer to IP OTC.
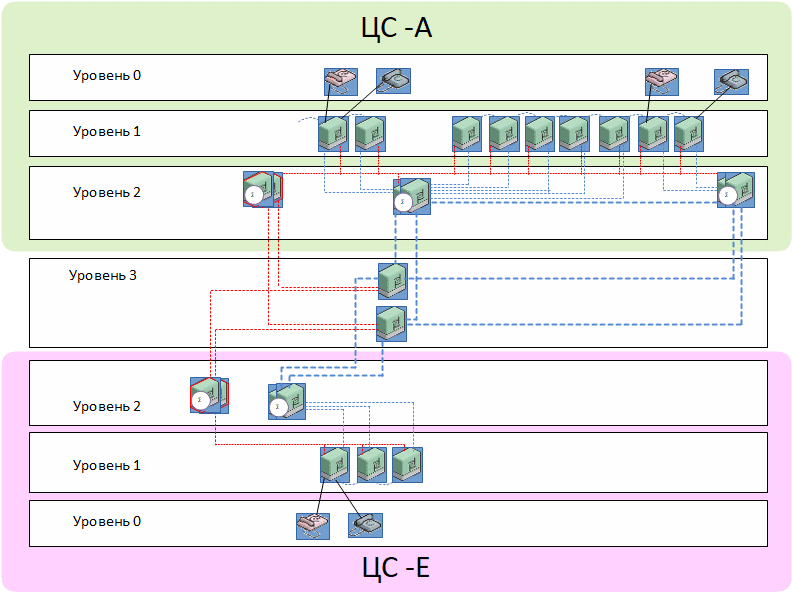
Image 2: An example of connection between edge points
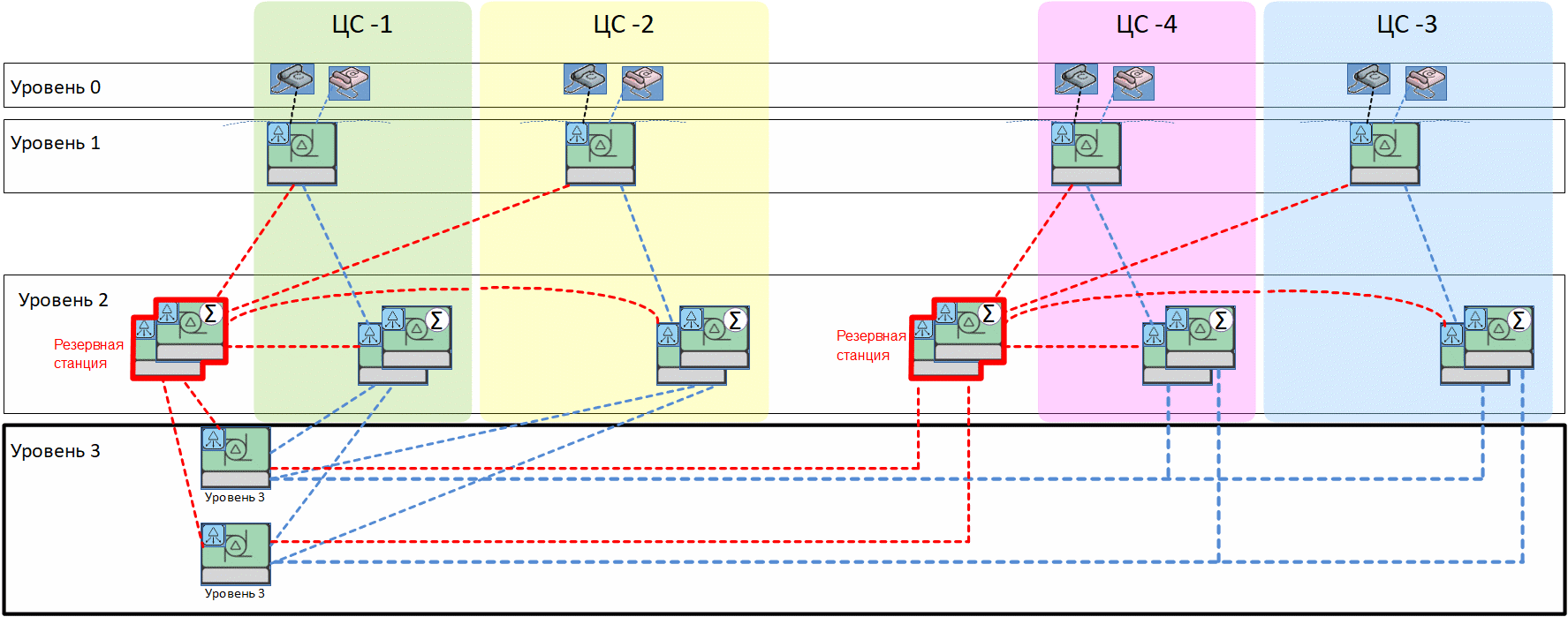
Image 3: An example of connection between TS
Copyright © 2020 - All Rights Reserved - Venisat Technology Limited
